Presentation
- Interfaces de usuario
- Interfaces con otras aplicaciones
Business
- Toda la lógica que involucra toda operación en nuestra aplicación.
- Componentes reutilizables que pueden servir para distintas aplicaciones.
Integration
- Bases de datos
- Legacy Systems
Problema
Se desean tranferir múltiples elementos de datos a través de capas.
Características
Solución
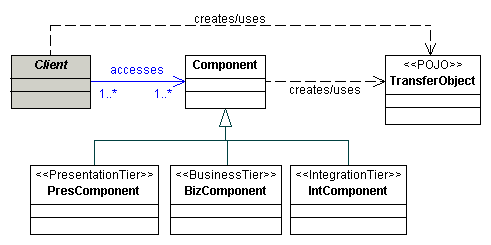
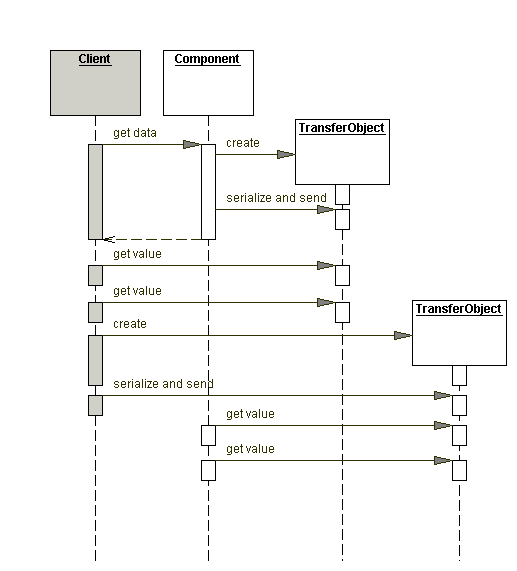
Usar un Transfer Object para llevar múltiples elementos a través de una capa.
Class diagram
 |
Sequence diagram
 |
Estrategias
Efectos
1:Example 8.1 CustomerTO.java: Transfer Object Used by CustomerDAO and Its Clients 2:package com.corej2eepatterns.to; 3: 4:public class CustomerTO implements java.io.Serializable { 5: private String id; 6: private String name; 7: private String address; 8: . . . 9: 10: public String getId(){ return id; } 11: public void setId(String id){ this.id = id; } 12: public String getName(){ return name; } 13: public void setName(String name){ this.name = name; } 14: public String getAddress(){ return address; } 15: public void setAddress(String address){ 16: this.address = address; 17: } 18: // other getters and setters 19: . . . 20:} |
Problema
Se desea encapsular acceso a datos y manipulación de los mismos en capas separadas.
Características
Solución
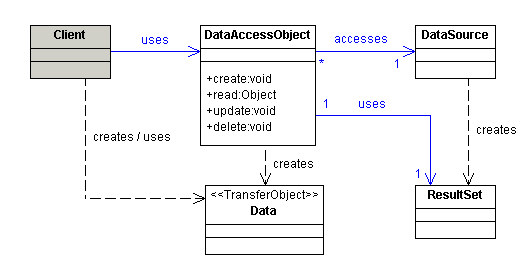
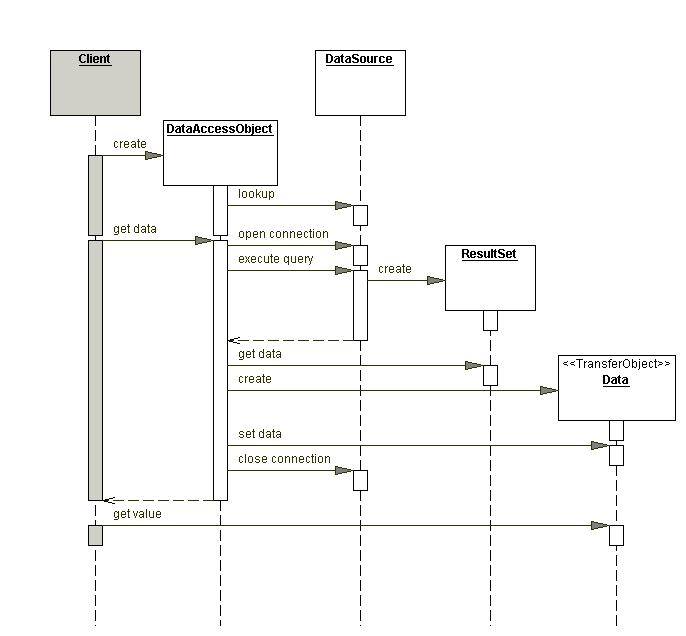
Emplear un Data Access Object DAO para abstraer y encapsular todos los accesos al almacenamiento persistente. El Data Access Object maneja las conexiones para guardar y recuperar datos.
Class diagram
 |
Sequence diagram
 |
Estrategias
Efectos
1:Example 8.2 CustomerDAO.java: Data Access Object 2:package com.corej2eepatterns.dao; 3: 4:// imports 5: 6:public class CustomerDAO { 7: protected static final String FIELDS_INSERT = 8: "customer_name, customer_address, " + 9: "customer_contact, customer_phone, customer_email"; 10: 11: protected static final String FIELDS_RETURN = 12: "customer_id, " + FIELDS_INSERT; 13: 14: protected static String INSERT_SQL = 15: "insert into customer ( " + FIELDS_INSERT + 16: " ) " + "values ( ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)"; 17: 18: protected static String SELECT_SQL = "select " + 19: FIELDS_RETURN + 20: " from customer where customer_id = ? "; 21: 22: protected static String UPDATE_SQL = 23: "update customer set customer_name = ?, " + 24: "customer_address = ?, customer_contact = ?, " + 25: "customer_phone = ?, customer_email = ? " + 26: "where customer_id = ? "; 27: 28: protected static String DELETE_SQL = 29: "delete from Customer where customer_id = ? "; 30: 31: // the data source used to connect to the back-end database 32: private DataSource datasource; 33: 34: public CustomerDAO() throws DAOException { 35: try { 36: // Shown here for clarity only. Typically, looking 37: // up a data source is done by a Service Locator 38: // and the DAO just uses the Service Locator to 39: // obtain a data source. 40: InitialContext initialContext = 41: new InitialContext(); 42: datasource = (DataSource) initialContext.lookup( 43: OracleDAOFactory.DATASOURCE_DB_NAME); 44: } catch (NamingException e) { 45: throw new DAOException ( 46: "Cannot locate data source at " + 47: DAOFactory.DATASOURCE_DB_NAME, e); 48: } 49: } 50: 51: public String create(CustomerTO cust) throws DAOException { 52: // initialize variables 53: Connection con = getConnection(); 54: String customerId = null; 55: 56: PreparedStatement prepStmt = null; 57: try { 58: // create and setup statement 59: prepStmt = con.prepareStatement(INSERT_SQL); 60: int i = 1; 61: prepStmt.setString(i++, cust.getName()); 62: prepStmt.setString(i++, cust.getAddress()); 63: . . . 64: 65: // execute the statement 66: prepStmt.executeUpdate(); 67: 68: // obtain the newly created customer id value 69: . . . 70: 71: } catch (Exception e) { 72: // handle exception 73: } finally { 74: // close connections 75: } 76: 77: // return the newly created customer id value 78: return customerId; 79: } 80: 81: public CustomerTO find(String customerId) 82: throws DAOException { 83: // initialize variables 84: CustomerTO cust = null; 85: Connection con = getConnection(); 86: PreparedStatement prepStmt = null; 87: ResultSet rs = null; 88: 89: try { 90: // setup statement and retrieve results 91: prepStmt = con.prepareStatement(SELECT_SQL); 92: prepStmt.setString(1, customerId); 93: rs = prepStmt.executeQuery(); 94: if (rs.next()) { 95: //create the transfer object using data from rs 96: cust = new CustomerTO(); 97: cust.setId(rs.getString(1)); 98: cust.setName(rs.getString(2)); 99: . . . 100: } 101: } catch (Exception e) { 102: // handle exception 103: } finally { 104: // close connections 105: } 106: return cust; 107: } 108: 109: public void update(CustomerTO cust) throws DAOException { 110: Connection con = null; 111: PreparedStatement prepStmt = null; 112: try { 113: // prepare statement 114: con = getConnection(); 115: 116: prepStmt = con.prepareStatement(UPDATE_SQL); 117: int i = 1; 118: 119: // add fields first 120: prepStmt.setString(i++, cust.getName()); 121: prepStmt.setString(i++, cust.getAddress()); 122: . . . 123: 124: // now add where parameters 125: prepStmt.setString(i++, cust.getId()); 126: int rowCount = prepStmt.executeUpdate(); 127: prepStmt.close(); 128: if (rowCount == 0) { 129: throw new DAOException( 130: "Update Error:Customer Id:" + cust.getId()); 131: } 132: } catch (Exception e) { 133: // handle exception 134: } finally { 135: // close connections 136: } 137: } 138: 139: public void delete(String customerId) throws Exception { 140: // setup variables 141: Connection con = getConnection(); 142: PreparedStatement prepStmt = null; 143: 144: try { 145: // execute database update 146: prepStmt = con.prepareStatement(DELETE_SQL); 147: prepStmt.setString(1, customerId); 148: prepStmt.executeUpdate(); 149: } catch (Exception e) { 150: // handle exception 151: } finally { 152: // close connections 153: } 154: } 155: 156: // other methods for finders, etc. 157: . . . 158:} |